Ginger #
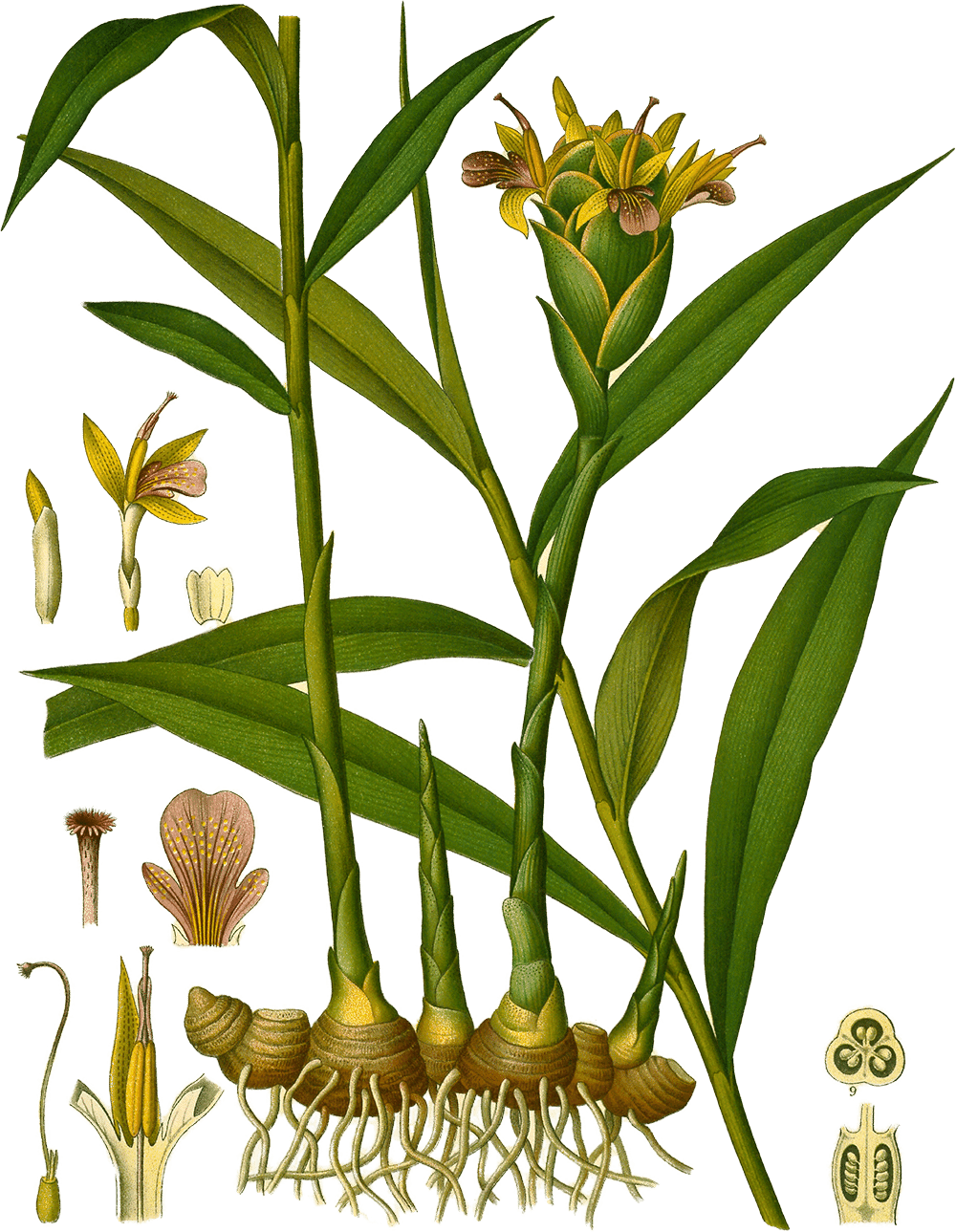
Illustration of Zingiber officinale Roscoe from Köhler's Medizinal-Pflanzen (1887)
Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) is a culinary and medicinal spice from the Zingiberaceae family,1 originating in the region(s) of South East Asia; India (secondary).2 It is used for its rhizome, primarily for Asian cooking; anti-emetic. Its aroma is described as fiery, pungent, with a heat index of 7.3
| English | Arabic | Chinese | Hungarian |
|---|---|---|---|
| ginger | زنجبيل | 薑 | gyömbér |
Overview #
| id | ginger |
|---|---|
| species name | Zingiber officinale Roscoe |
| family | Zingiberaceae |
| part used | rhizome |
| macroarea | Asia |
| region of origin | South East Asia; India (secondary) |
| cultivation | India; Jamaica; Nigeria; Sierra Leone |
| color | light yellow when fresh, beige when powdered |
| botanical database | POWO |
Etymologies #
English ginger, ca. 925 < reinforced by Old French gingivere, gingibre ‘ginger’ < Medieval Latin gingiber ‘ginger’ < Latin zingiber ‘ginger’ < Ancient Greek ziggiberis ‘ginger’ < Pali siṅgivera ‘ginger’; cf. cognates Sanskrit शृङ्गवेर < Dravidian * cinki-wēr ‘ginger’, South dravidian nominal compound from the etyma of Tamil and Malayalam iñci (both with regular loss of an initial sibilant) + vēr (Proto-Dravidian wēr); the base of * cinki is a loanword < unknown language ? ‘ginger’, unidentified Southeast Asian language; cf. cognates Khasi sying /sʔiŋ/, Thai khing, Vietnamese gừng, Chinese jiāng < Proto-Sino-Tibetan * kjaŋ ‘ginger’
Arabic زنجبيل zanjabīl ‘ginger’, 609-632 < Classical Syriac ܙܢܓܒܝܠ zangabīl ‘ginger’ < Pahlavi singibēr ‘ginger’, or via another Middle Iranian language < Sauraseni Prakrit 𑀲𑀺𑀁𑀕𑀺𑀯𑁂𑀭 siṃgivera ‘ginger’ < Sanskrit शृङ्गवेर śṛṅgavera ‘ginger’ < Dravidian * cinki-wēr ‘ginger’, South dravidian nominal compound from the etyma of Tamil and Malayalam iñci (both with regular loss of an initial sibilant) + vēr (Proto-Dravidian wēr); the base of * cinki is a loanword < unknown language ? ‘ginger’, unidentified Southeast Asian language; cf. cognates Khasi sying /sʔiŋ/, Thai khing, Vietnamese gừng, Chinese jiāng < Proto-Sino-Tibetan * kjaŋ ‘ginger’
Mandarin Chinese 薑 jiāng ‘ginger’, -221 < Old Chinese 䕬 OC / *kaŋ/ ‘ginger’ < Proto-Sino-Tibetan * kjaŋ ‘ginger’; cf. Burmese ချင်း hkyang:
Names #
English #
| term | source |
|---|---|
| ginger | OED |
| black ginger | OED |
| ginger root | OED |
| ginger spice | OED |
| green ginger | OED |
| white ginger | OED |
Arabic #
| script | term | literal | source |
|---|---|---|---|
| زنجبيل | zanjabīl | Wehr, 1976 | |
| جنزبيل | janzabīl | Wehr, 1976 |
Chinese #
| script | term | literal | source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 薑 | jiāng | ginger | Kleeman, 2010 |
| 幹薑 | gānjiāng | dry-ginger | Defrancis, 2003 |
| 鮮薑 | xiānjiāng | fresh-ginger | Defrancis, 2003 |
POWO. (2022). Plants of the World Online (Botanical Database). Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/ ↩︎
van Wyk, B.-E. (2014). Culinary Herbs and Spices of the World. University of Chicago Press, joint publication with the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. https://doi.org/10.7208/chicago/9780226091839.001.0001 ↩︎
Medicinal Spices Exhibit. (2002). UCLA Biomedical Library: History & Special Collections. https://unitproj.library.ucla.edu/biomed/spice/index.cfm?spicefilename=taste.txt&itemsuppress=yes&displayswitch=0 ↩︎