Fennel #
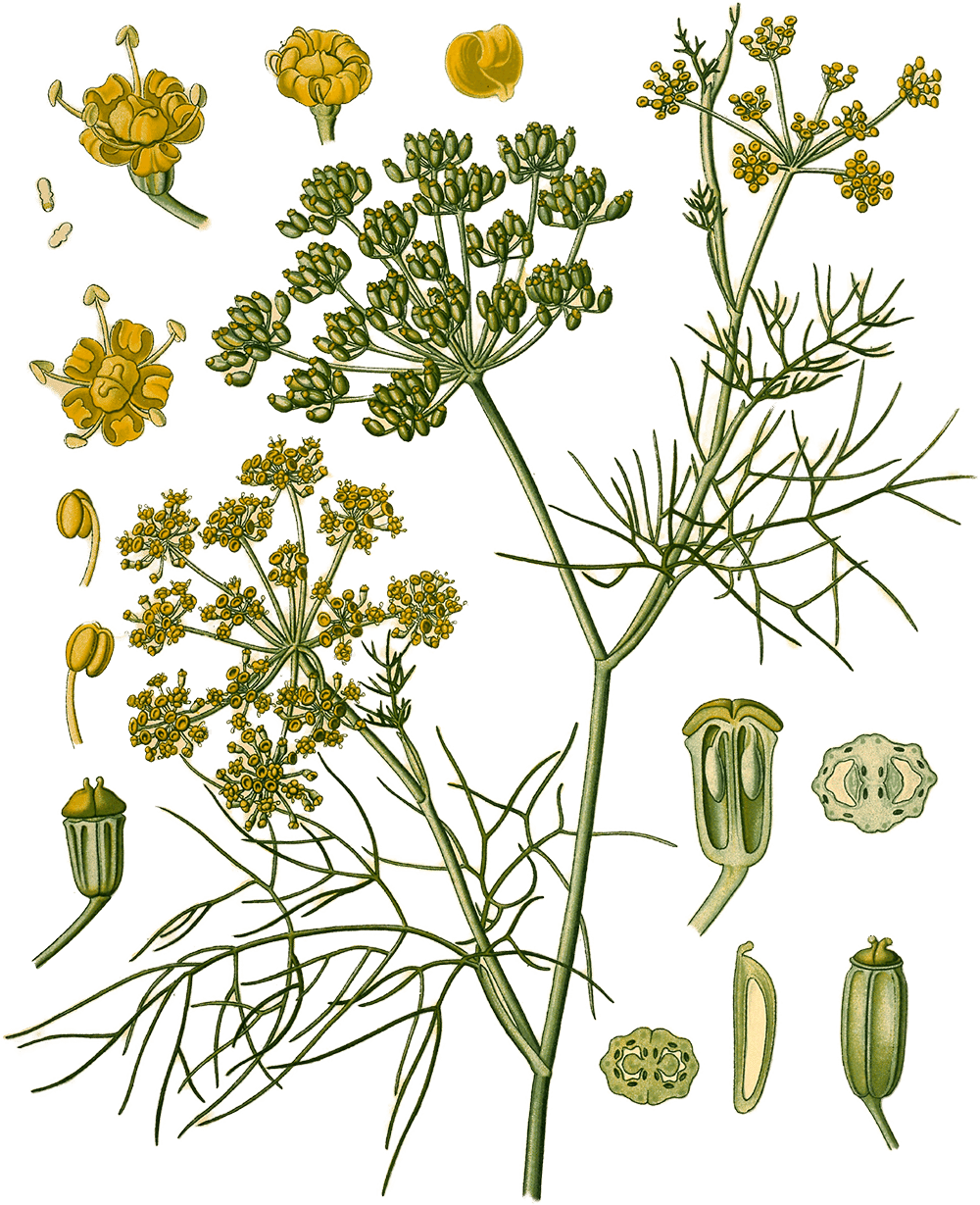
Illustration of Foeniculum vulgare Mill. from Köhler's Medizinal-Pflanzen (1887)
Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Mill.) is a culinary spice and herb and vegetable from the Apiaceae family,1 originating in the region(s) of Med.2 It is used for its fruit and leaf, primarily for fish, breads, sausages; colic. Its aroma is described as licorice-like, warm, with a heat index of 1.3
| English | Arabic | Chinese | Hungarian |
|---|---|---|---|
| fennel | شمر | 茴香 | édeskömény |
Overview #
| id | fennel |
|---|---|
| species name | Foeniculum vulgare Mill. |
| family | Apiaceae |
| part used | fruit; leaf |
| macroarea | Med.; W. Asia |
| region of origin | Med |
| cultivation | Argentina; Bulgaria; Germany; Greece; India; Lebanon |
| color | light green to light brown |
| botanical database | POWO |
Etymologies #
English fennel, a. 700 < Old English fenol, a. 700 < Latin faeniculum, via Vulgar Latin fēnoclum, fēnuclum substituted for classical Latin faeniculum, diminutive of faenum hay; cf. Old French fenoil (modern French fenouil), Provençal fenolh, Italian finocchio, Spanish hinojo.
Arabic شمر shamar ‘fennel’ < Aramaic simra ‘fennel’ < Akkadian šimru ‘fennel’
Mandarin Chinese 茴香 huíxiāng ‘fennel’ [hui-spice ], 茴 hui refers to fennel, anise, and related plants; it perhaps could be rendered as ‘muslim spice’ by way of its construction: 回 ‘Islam; Hui people’ + 艹 ‘grass, herb’ (Hu, 2005); or, phono semantic compund
Names #
English #
| term | source |
|---|---|
| fennel | OED |
| fennel-seed | OED |
| Indian fennel | OED |
| sweet fennel | OED |
Arabic #
| script | term | literal | source |
|---|---|---|---|
| شمر | shamar | Wehr, 1976 | |
| شمرة | shamra, shumra | Wehr, 1976 | |
| بسباس | basbās | Wehr, 1976 | |
| رازيانج | rāzyānj | ||
| شمار | shamār | Wehr, 1976 | |
| سنوت | sunūt |
Chinese #
| script | term | literal | source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 茴香 | huíxiāng | hui-spice | Kleeman, 2010 |
| 蘹香 | huáixiāng | huai-spice | |
| 甜茴香 | tiánhuíxiāng | sweet-fennel | |
| 小茴香 | xiǎohuíxiāng | small-anise |
POWO. (2022). Plants of the World Online (Botanical Database). Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/ ↩︎
van Wyk, B.-E. (2014). Culinary Herbs and Spices of the World. University of Chicago Press, joint publication with the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. https://doi.org/10.7208/chicago/9780226091839.001.0001 ↩︎
Medicinal Spices Exhibit. (2002). UCLA Biomedical Library: History & Special Collections. https://unitproj.library.ucla.edu/biomed/spice/index.cfm?spicefilename=taste.txt&itemsuppress=yes&displayswitch=0 ↩︎