Asafoetida #
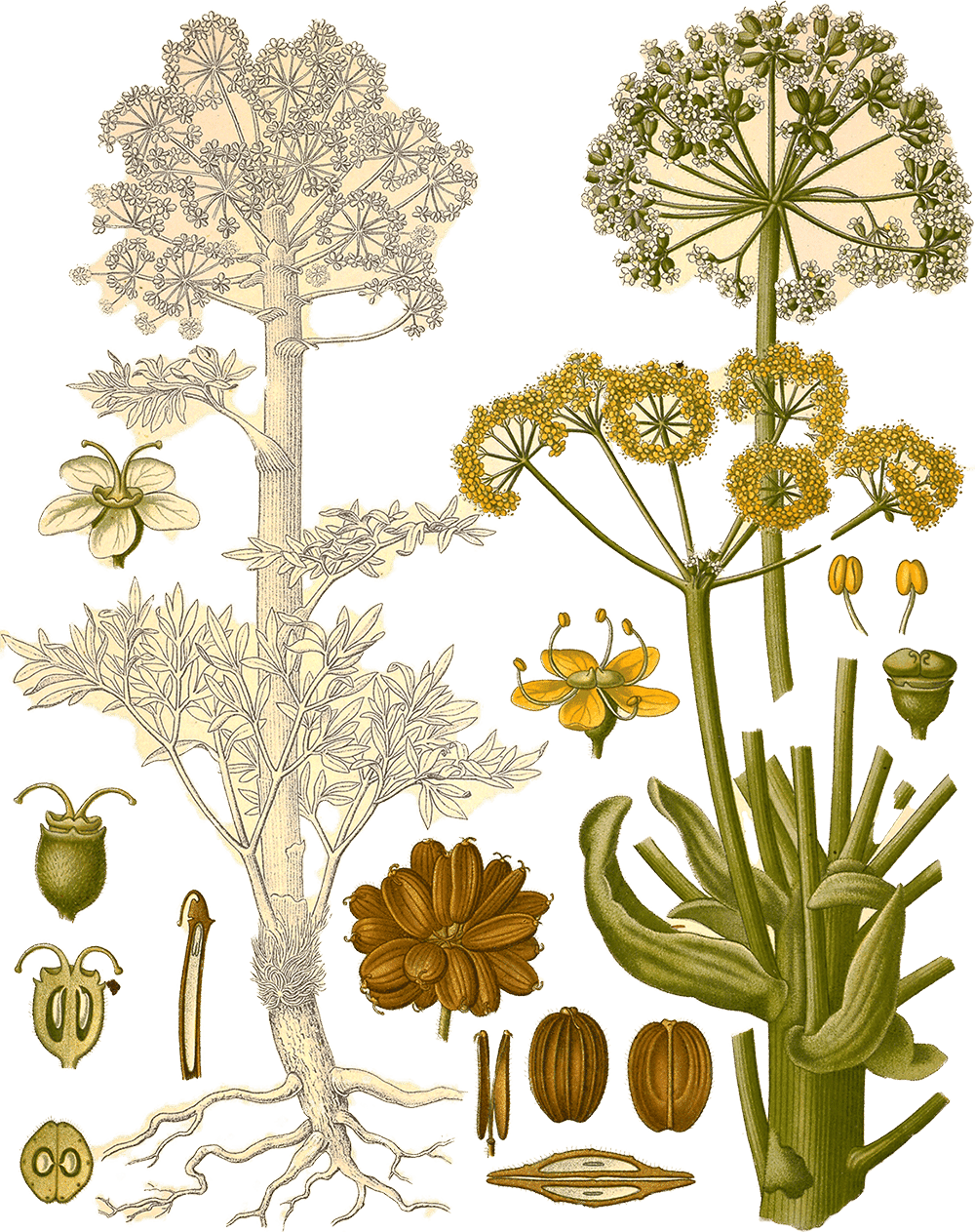
Illustration of Ferula foetida (Bunge) Regel from Köhler's Medizinal-Pflanzen (1887)
Asafoetida (Ferula foetida (Bunge) Regel) is a culinary and medicinal spice from the Apiaceae family,1 originating in the region(s) of Iran; W. and C. Asia.2 It is used for its gum-resin (latex), primarily for curries; expectorant. Its aroma is described as pungent, rotten, with a heat index of 1.3
| English | Arabic | Chinese | Hungarian |
|---|---|---|---|
| asafoetida | حلتیت | 阿魏 | ördöggyökér |
Overview #
| id | asafoetida |
|---|---|
| species name | Ferula foetida (Bunge) Regel |
| family | Apiaceae |
| part used | gum-resin (latex) |
| macroarea | Asia |
| region of origin | Iran; W. and C. Asia |
| cultivation | Iran; Afghanistan |
| color | from pale yellow to brown |
| botanical database | POWO |
Etymologies #
English asafoetida, a. 1398 < Medieval Latin asafoetida [stinking asa ] < from Persian āzā ‘mastic’, in a Lanized form, asa + Latin foetid ‘ill-smelling, stinking’, (feminine of fœtidus)
English hing ‘asafoetida’, 1599 < Hindi हींग hīng ‘asafoetida’ < Sanskrit हिङ्गु hiṅgu ‘asafoetida’; cf. cognates Sogdian ‘ynkw < Proto-Iranian * aṅgu-ǰatu- ‘resin-gum’; cf. Tokharian B, Khotanese
Arabic حلتيت ḥiltīt ‘asafoetida resin’; cf. cognates Hebrew ḥiltiṯ < Aramaic / ḥeltīṯā ‘id.’
Arabic أنجدان anjudān < Persian انگدان angudān < Proto-Iranian * aṅgu-ǰatu- ‘resin-gum’; cf. Tokharian B, Khotanese
Mandarin Chinese 阿魏 āwèi MC /ʔɑ ŋʉiH/ ‘asafoetida’ < Tokharian B ankwaṣ(ṭ) ‘asafoetida’ < Sogdian * angužat ‘asafoetida’ < Proto-Iranian * aṅgu-ǰatu- ‘resin-gum’
Mandarin Chinese 興蕖/興渠/興瞿 xīngqú MC /hɨŋ ɡɨʌ/ ‘asafoetida’, phonetic transcription < Sanskrit हिङ्गु hiṅgu ‘asafoetida’ < Proto-Iranian * aṅgu-ǰatu- ‘resin-gum’; cf. Tokharian B, Khotanese
Names #
English #
| term | source |
|---|---|
| asafoetida | OED |
| stinking gum | Peter, 2012 |
| devil’s dung | OED |
| hing | OED |
Arabic #
| script | term | literal | source |
|---|---|---|---|
| حلتیت | ḥiltīt | Wehr, 1976 | |
| أبو كبير | abū kabīr | big father | Wehr, 1976 |
| صمغ الأجذان | samgh al-anjudān | gum of anjudan | Baalbaki, 1995 |
| صمغ راتيناجي | samgh rātīnājī | rātīnājī gum | Baalbaki, 1995 |
| أنجدان | anjudān | Baalbaki, 1995 |
Chinese #
| script | term | literal | source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 阿魏 | āwèi | MDBG | |
| 阿虞 | ayü | Leung, 2019 | |
| 哈昔尼 | hāxīní | Leung, 2019 | |
| 黑黎提提 | hēilítítí | Rossabi, 2013 | |
| 形虞 | xíngyú | Leung, 2019 | |
| 興蕖/興渠/興瞿 | xīngqú | Leung, 2019 |
POWO. (2022). Plants of the World Online (Botanical Database). Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/ ↩︎
van Wyk, B.-E. (2014). Culinary Herbs and Spices of the World. University of Chicago Press, joint publication with the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. https://doi.org/10.7208/chicago/9780226091839.001.0001 ↩︎
Medicinal Spices Exhibit. (2002). UCLA Biomedical Library: History & Special Collections. https://unitproj.library.ucla.edu/biomed/spice/index.cfm?spicefilename=taste.txt&itemsuppress=yes&displayswitch=0 ↩︎