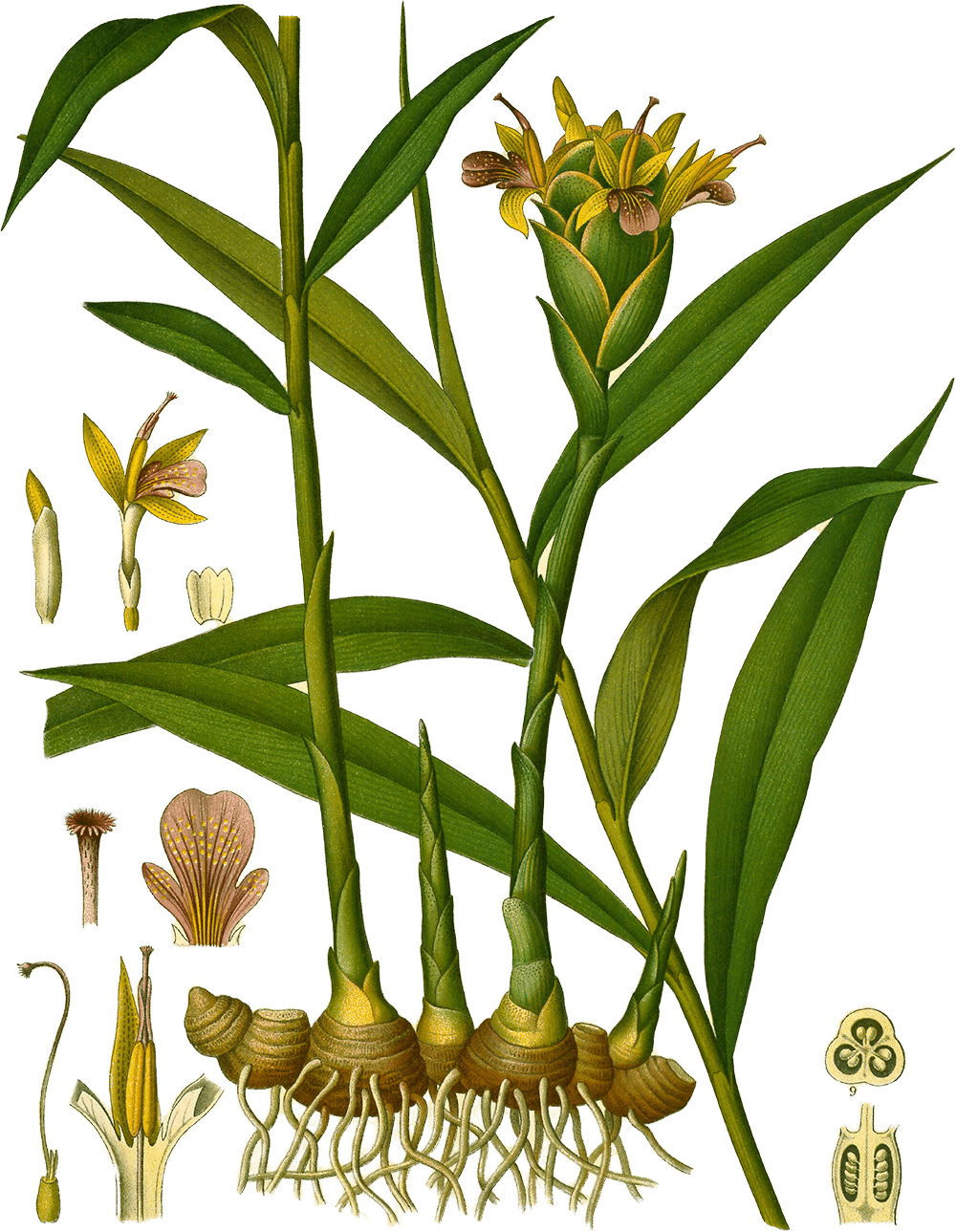
Ginger
The aromatic rhizomes of the ginger plant, fresh or dried, also known as ginger; common ginger. It is related to turmeric.
English: ginger · Hungarian: gyömbér · Arabic: زنجبيل · Hindi: अदरक · Chinese: 薑
Overview
| item | ginger |
|---|---|
| taxon | Zingiber officinale Roscoe |
| family | Zingiberaceae |
| regions | China, Indian Subcontinent |
| continents | Asia-Temperate, Asia-Tropical |
| part | rhizome |
| cultivation | India; Jamaica; Nigeria; Sierra Leone |
| botanical_database | POWO; GBIF; TROP; EOL |
GINGER is a culinary, and medicinal spice, cultivated for its rhizome. It is yielded from the plant Zingiber officinale Roscoe, a perennial or rhizomatous geophyte in the Zingiberaceae family, growing in seasonally dry tropical biome, with a native range of India to SC. China.1
It is used primarily in Asian cooking; anti-emetic. Its aroma is described as fiery, pungent, with a heat index of 7.2
See more in ( Citation: POWO, 2024 POWO (2024). Plants of the world online. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved from http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/ ; Citation: Petruzzello, 2021 Petruzzello, M. (2021). List of herbs and spices. Retrieved from https://www.britannica.com/topic/list-of-herbs-and-spices-2024392 ; Citation: Wyk, 2014 Wyk, B. (2014). Culinary herbs and spices of the world. University of Chicago Press, joint publication with the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. ; Citation: Dalby, 2000 Dalby, A. (2000). Dangerous tastes: the story of spices. University of California Press. ; Citation: Hill, 2004 Hill, T. (2004). The contemporary encyclopedia of herbs and spices: Seasonings for the global kitchen. J. Wiley. ; Citation: Anderson, 2023 Anderson, I. (2023). The history and natural history of spices: the 5000-year search for flavour. The History Press. )
Illustration of Zingiber officinale from Köhler’s Medizinal-Pflanzen ( Citation: 1887 Köhler, H. (1887). Köhler’s Medizinal-Pflanzen in naturgetreuen Abbildungen mit kurz erläuterndem Texte: Atlas zur Pharmacopoea germanica, austriaca, belgica, danica, helvetica, hungarica, rossica, suecica, Neerlandica, British pharmacopoeia, zum Codex medicamentarius, sowie zur Pharmacopoeia of the United States of America. Franz Eugen Köhler. Retrieved from https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/623 ) II 172.
Distribution
Native and introduced habitats of Zingiber officinale3
Native areas: China South-Central, Assam, East Himalaya, India
Introduced areas: Gulf of Guinea Is., Comoros, Mauritius, Madagascar, Réunion, Rodrigues, Hainan, China Southeast, Taiwan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Andaman Is., Cambodia, Myanmar, Nicobar Is., Thailand, Vietnam, Borneo, Lesser Sunda Is., Malaya, Philippines, New Guinea, Solomon Is., Queensland, Vanuatu, Caroline Is., Mexico Southwest, Costa Rica, Honduras, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Haiti, Leeward Is., Puerto Rico, Trinidad-Tobago, Windward Is.
Bibliography
- Anderson (2023)
- Anderson, I. (2023). The history and natural history of spices: the 5000-year search for flavour. The History Press.
- Dalby (2000)
- Dalby, A. (2000). Dangerous tastes: the story of spices. University of California Press.
- Hill (2004)
- Hill, T. (2004). The contemporary encyclopedia of herbs and spices: Seasonings for the global kitchen. J. Wiley.
- Köhler (1887)
- Köhler, H. (1887). Köhler’s Medizinal-Pflanzen in naturgetreuen Abbildungen mit kurz erläuterndem Texte: Atlas zur Pharmacopoea germanica, austriaca, belgica, danica, helvetica, hungarica, rossica, suecica, Neerlandica, British pharmacopoeia, zum Codex medicamentarius, sowie zur Pharmacopoeia of the United States of America. Franz Eugen Köhler. Retrieved from https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/623
- Petruzzello (2021)
- Petruzzello, M. (2021). List of herbs and spices. Retrieved from https://www.britannica.com/topic/list-of-herbs-and-spices-2024392
- POWO (2024)
- POWO (2024). Plants of the world online. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved from http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/
- Wyk (2014)
- Wyk, B. (2014). Culinary herbs and spices of the world. University of Chicago Press, joint publication with the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
Medicinal Spices Exhibit. (2002). UCLA Biomedical Library: History & Special Collections. https://unitproj.library.ucla.edu/biomed/spice/index.cfm?spicefilename=taste.txt&itemsuppress=yes&displayswitch=0 ↩︎