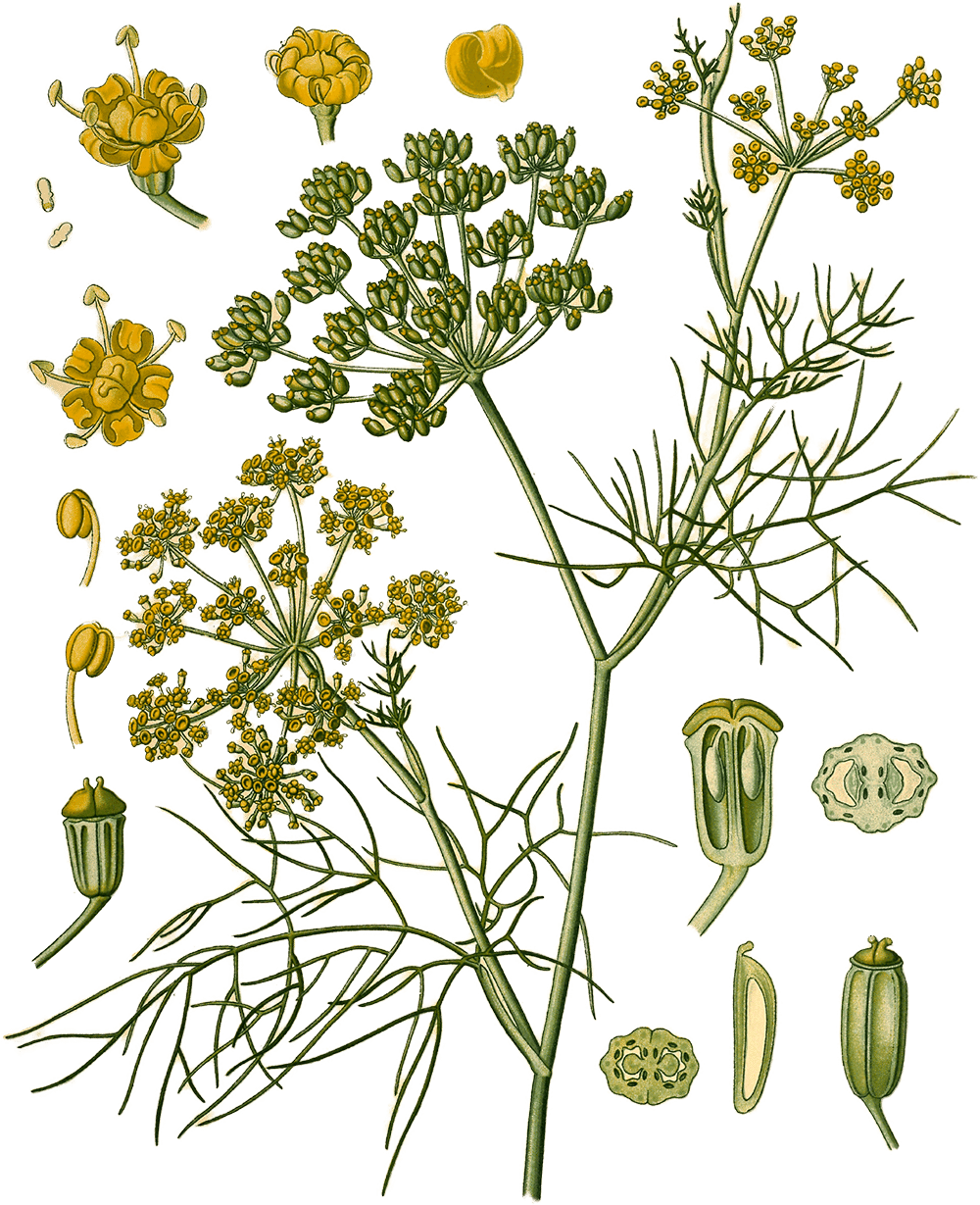
Fennel
The dried fruits of a perennial herb, also known as fennel (seeds).
English: fennel · Hungarian: édeskömény · Arabic: شمر · Hindi: सौंफ़ · Chinese: 茴香
Overview
| item | fennel |
|---|---|
| taxon | Foeniculum vulgare Mill. |
| family | Apiaceae |
| regions | Southwestern Europe, Southeastern Europe, Northern Africa, Northeast Tropical Africa, Middle Asia, Caucasus, Western Asia, Arabian Peninsula, Indian Subcontinent |
| continents | Europe, Africa, Asia-Temperate, Asia-Tropical |
| part | fruit |
| cultivation | Argentina; Bulgaria; Germany; Greece; India; Lebanon |
| botanical_database | POWO |
FENNEL is a culinary spice, cultivated for its fruit. It is yielded from the plant Foeniculum vulgare Mill., a perennial in the Apiaceae family, growing in temperate biome, with a native range of Medit. to Ethiopia and W. Nepal.1
It is used primarily in fish, breads, sausages; colic. Its aroma is described as licorice-like, warm, with a heat index of 1.2
See more in ( Citation: POWO, 2024 POWO (2024). Plants of the world online. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved from http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/ ; Citation: Petruzzello, 2021 Petruzzello, M. (2021). List of herbs and spices. Retrieved from https://www.britannica.com/topic/list-of-herbs-and-spices-2024392 ; Citation: Wyk, 2014 Wyk, B. (2014). Culinary herbs and spices of the world. University of Chicago Press, joint publication with the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. ; Citation: Hill, 2004 Hill, T. (2004). The contemporary encyclopedia of herbs and spices: Seasonings for the global kitchen. J. Wiley. ; Citation: Anderson, 2023 Anderson, I. (2023). The history and natural history of spices: the 5000-year search for flavour. The History Press. )
Illustration of Foeniculum vulgare from Köhler’s Medizinal-Pflanzen ( Citation: 1887 Köhler, H. (1887). Köhler’s Medizinal-Pflanzen in naturgetreuen Abbildungen mit kurz erläuterndem Texte: Atlas zur Pharmacopoea germanica, austriaca, belgica, danica, helvetica, hungarica, rossica, suecica, Neerlandica, British pharmacopoeia, zum Codex medicamentarius, sowie zur Pharmacopoeia of the United States of America. Franz Eugen Köhler. Retrieved from https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/623 ) II 88.
Distribution
Native and introduced habitats of Foeniculum vulgare3
Native areas: Baleares, Corse, France, Portugal, Sardegna, Spain, Albania, Bulgaria, Greece, Italy, Kriti, Sicilia, Turkey-in-Europe, Yugoslavia, Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Turkmenistan, Tadzhikistan, Uzbekistan, North Caucasus, Transcaucasus, Afghanistan, Cyprus, East Aegean Is., Iran, Iraq, Lebanon-Syria, Palestine, Sinai, Turkey, Gulf States, Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Nepal, Pakistan, West Himalaya
Introduced areas: Denmark, Finland, Great Britain, Ireland, Norway, Sweden, Austria, Belgium, Czechoslovakia, Germany, Hungary, Netherlands, Poland, Switzerland, Romania, Krym, Central European Rus, South European Russi, Ukraine, Cameroon, Gulf of Guinea Is., Djibouti, Somalia, Sudan, Kenya, Tanzania, Angola, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Cape Provinces, Lesotho, KwaZulu-Natal, Northern Provinces, St.Helena, Mauritius, Réunion, Rodrigues, Kazakhstan, China South-Central, Hainan, Inner Mongolia, China North-Central, China Southeast, Mongolia, Korea, Taiwan, Assam, Bangladesh, East Himalaya, India, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, Jawa, Norfolk Is., New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, Western Australia, New Zealand North, New Zealand South, Fiji, Niue, Society Is., Marianas, Hawaii, Alberta, British Columbia, Ontario, Québec, Oregon, Washington, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, Missouri, Nebraska, Wisconsin, Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, Michigan, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode I., West Virginia, Arizona, California, Nevada, Utah, New Mexico, Texas, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, Mexico Northwest, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Bahamas, Bermuda, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Haiti, Jamaica, Leeward Is., Puerto Rico, Windward Is., Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Brazil Southeast, Brazil South, Argentina Northeast, Argentina South, Argentina Northwest, Chile Central, Chile North, Chile South, Juan Fernández Is., Paraguay, Uruguay, Amsterdam-St.Paul Is
Bibliography
- Anderson (2023)
- Anderson, I. (2023). The history and natural history of spices: the 5000-year search for flavour. The History Press.
- Hill (2004)
- Hill, T. (2004). The contemporary encyclopedia of herbs and spices: Seasonings for the global kitchen. J. Wiley.
- Köhler (1887)
- Köhler, H. (1887). Köhler’s Medizinal-Pflanzen in naturgetreuen Abbildungen mit kurz erläuterndem Texte: Atlas zur Pharmacopoea germanica, austriaca, belgica, danica, helvetica, hungarica, rossica, suecica, Neerlandica, British pharmacopoeia, zum Codex medicamentarius, sowie zur Pharmacopoeia of the United States of America. Franz Eugen Köhler. Retrieved from https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/623
- Petruzzello (2021)
- Petruzzello, M. (2021). List of herbs and spices. Retrieved from https://www.britannica.com/topic/list-of-herbs-and-spices-2024392
- POWO (2024)
- POWO (2024). Plants of the world online. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved from http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/
- Wyk (2014)
- Wyk, B. (2014). Culinary herbs and spices of the world. University of Chicago Press, joint publication with the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
Medicinal Spices Exhibit. (2002). UCLA Biomedical Library: History & Special Collections. https://unitproj.library.ucla.edu/biomed/spice/index.cfm?spicefilename=taste.txt&itemsuppress=yes&displayswitch=0 ↩︎