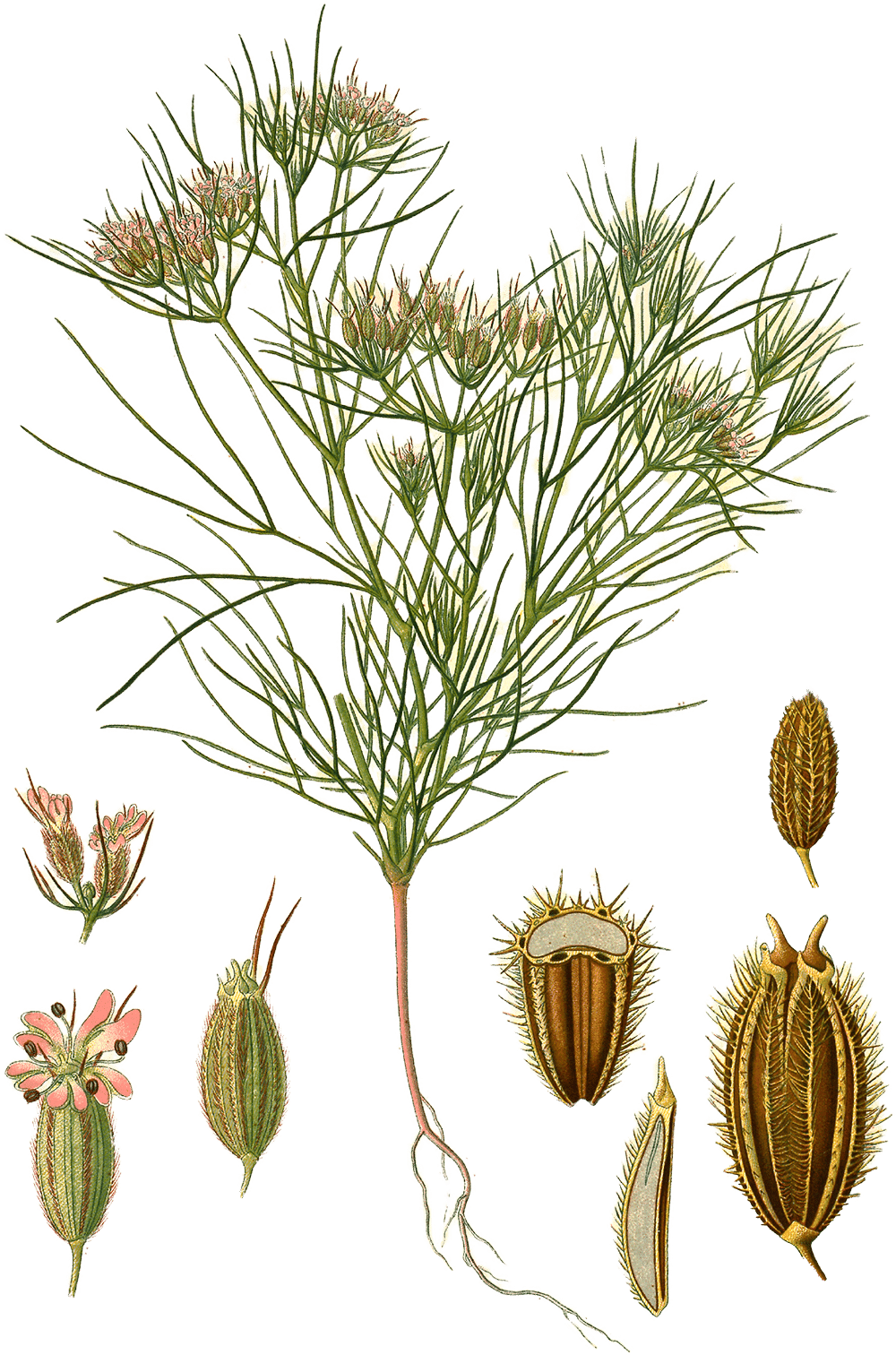
Cumin
The dried seeds of a West Asian flowering plant, also known as brown cumin. It is related to caraway.
English: cumin · Hungarian: római kömény · Arabic: كمون · Hindi: जीरा · Chinese: 孜然 ·
Overview
| item | cumin |
|---|---|
| taxon | Cuminum cyminum L. |
| family | Apiaceae |
| regions | Western Asia |
| continents | Asia-Temperate |
| part | fruit |
| cultivation | India; Iran; Lebanon |
| botanical_database | POWO; GBIF; EOL |
CUMIN is a culinary spice, cultivated for its fruit. It is yielded from the plant Cuminum cyminum L., a annual in the Apiaceae family, growing in subtropical biome, with a native range of Iraq to Afghanistan.1
It is used primarily in curries, breads; colic. Its aroma is described as peppery, aromatic, with a heat index of 4.2
See more in ( Citation: POWO, 2024 POWO (2024). Plants of the world online. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved from http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/ ; Citation: Petruzzello, 2021 Petruzzello, M. (2021). List of herbs and spices. Retrieved from https://www.britannica.com/topic/list-of-herbs-and-spices-2024392 ; Citation: Wyk, 2014 Wyk, B. (2014). Culinary herbs and spices of the world. University of Chicago Press, joint publication with the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. ; Citation: Dalby, 2000 Dalby, A. (2000). Dangerous tastes: the story of spices. University of California Press. ; Citation: Hill, 2004 Hill, T. (2004). The contemporary encyclopedia of herbs and spices: Seasonings for the global kitchen. J. Wiley. ; Citation: Anderson, 2023 Anderson, I. (2023). The history and natural history of spices: the 5000-year search for flavour. The History Press. )
Illustration of Cuminum cyminum from Köhler’s Medizinal-Pflanzen ( Citation: 1887 Köhler, H. (1887). Köhler’s Medizinal-Pflanzen in naturgetreuen Abbildungen mit kurz erläuterndem Texte: Atlas zur Pharmacopoea germanica, austriaca, belgica, danica, helvetica, hungarica, rossica, suecica, Neerlandica, British pharmacopoeia, zum Codex medicamentarius, sowie zur Pharmacopoeia of the United States of America. Franz Eugen Köhler. Retrieved from https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/623 ) III 23.
Distribution
Native and introduced habitats of Cuminum cyminum3
Native areas: Afghanistan, Iran, Iraq
Introduced areas: France, Spain, Bulgaria, Sicilia, Algeria, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia, Benin, Eritrea, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Transcaucasus, Lebanon-Syria, Saudi Arabia, Xinjiang, Bangladesh, East Himalaya, India, Pakistan, Andaman Is., Laos, Nicobar Is., Massachusetts, Texas, Mexico Northeast
Bibliography
- Anderson (2023)
- Anderson, I. (2023). The history and natural history of spices: the 5000-year search for flavour. The History Press.
- Dalby (2000)
- Dalby, A. (2000). Dangerous tastes: the story of spices. University of California Press.
- Hill (2004)
- Hill, T. (2004). The contemporary encyclopedia of herbs and spices: Seasonings for the global kitchen. J. Wiley.
- Köhler (1887)
- Köhler, H. (1887). Köhler’s Medizinal-Pflanzen in naturgetreuen Abbildungen mit kurz erläuterndem Texte: Atlas zur Pharmacopoea germanica, austriaca, belgica, danica, helvetica, hungarica, rossica, suecica, Neerlandica, British pharmacopoeia, zum Codex medicamentarius, sowie zur Pharmacopoeia of the United States of America. Franz Eugen Köhler. Retrieved from https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/623
- Petruzzello (2021)
- Petruzzello, M. (2021). List of herbs and spices. Retrieved from https://www.britannica.com/topic/list-of-herbs-and-spices-2024392
- POWO (2024)
- POWO (2024). Plants of the world online. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved from http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/
- Wyk (2014)
- Wyk, B. (2014). Culinary herbs and spices of the world. University of Chicago Press, joint publication with the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
Medicinal Spices Exhibit. (2002). UCLA Biomedical Library: History & Special Collections. https://unitproj.library.ucla.edu/biomed/spice/index.cfm?spicefilename=taste.txt&itemsuppress=yes&displayswitch=0 ↩︎